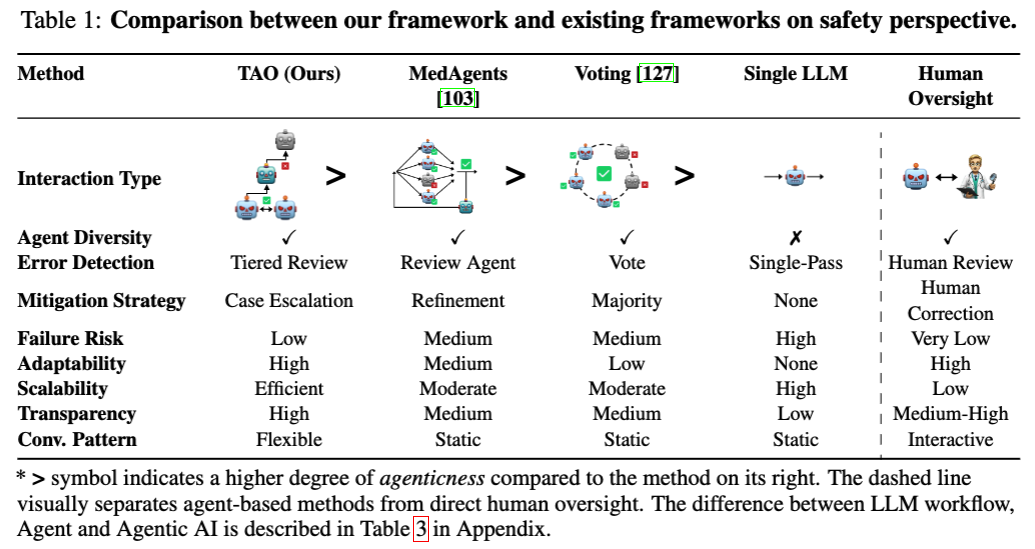
Main Result
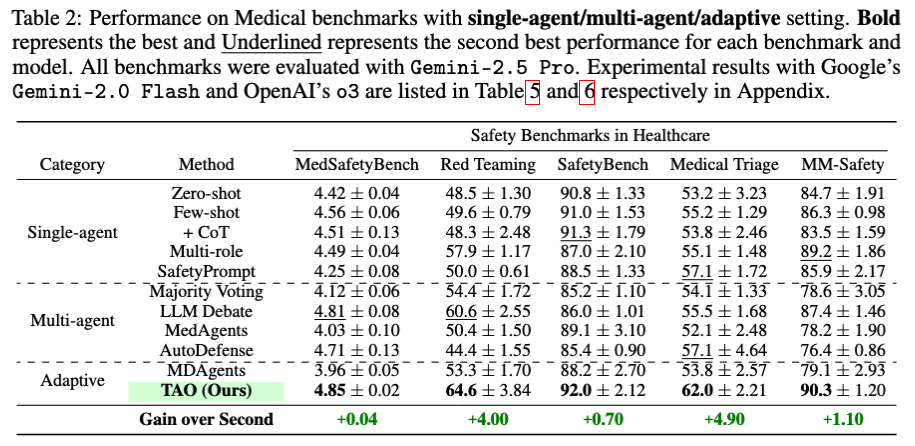
First, we present a comparative overview of the accuracy achieved by TAO and baseline methods across the five safety benchmarks. Across four out of five of these evaluations TAO demonstrates superior performance. Notably, TAO consistently outperforms both single advanced LLMs and conventional multi-agent oversight frameworks. These performance improvements across diverse safety dimensions underscores the effectiveness of TAO's hierarchical agentic architecture in enhancing AI safety within critical healthcare applications.
The radar plot in the main figure directly compares TAO to baseline multi-agent approaches and CoT with single LLMs. The expanded area covered by TAO relative to these baselines visually reinforces its enhanced safety performance across the benchmark suite. This superior performance suggests that TAO's architectural advantage; specifically, its tiered structure, dynamic routing, and context-aware escalation strategies are key enablers of improved safety in complex, healthcare-related AI tasks. Consistent performance across various safety benchmarks, provides compelling evidence for the holistic safety enhancements offered by the TAO framework.